One: Bell Labs 1947
Solid State at Last

Source: https://www.computerhistory.org/revolution/digital-logic/12/273
Making a transistor.
Chemistry, electricity, positive and negative charges, holes and free electrons. Semiconducting materials residing between conductors and insulators but easy to manipulate with a base or tap. Look for the emitters that handles the main current and the collector where the electrons travel.
What is happening inside the computer?
All those transistors carrying information in the forms of on/off, high voltage/low voltage. Storing a bit and changing with a bit.
Transistor as a key part of digital logic.
Traiterous Eight and the Fairchildren in Silicon Valley

Just as the transistor multiplied, so too did offshoot companies of Fairchild called Fairchildren develop more applications and develop the technology.
Field Effect with MOS (Metal oxide silicon) Transistor
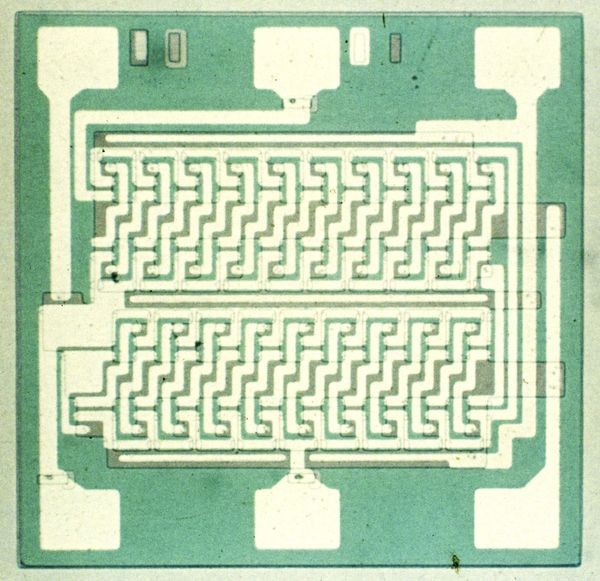
This was the first commercial MOS IC: Robert Norman’s 20-bit shift register using 120 p-channel transistors. 1964
The story rapidly accelerates, Computer History website for the history of digital logic. https://www.computerhistory.org/revolution/digital-logic/12/275
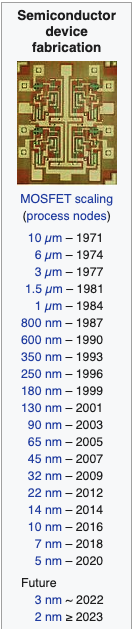
Shrinking and Fitting More
As more transistors are fit onto a silicon chip the size decreases. Moore’s Law continues to measure roughly the progress of how many transistors can be embedded on silicon.
We count by transistors.
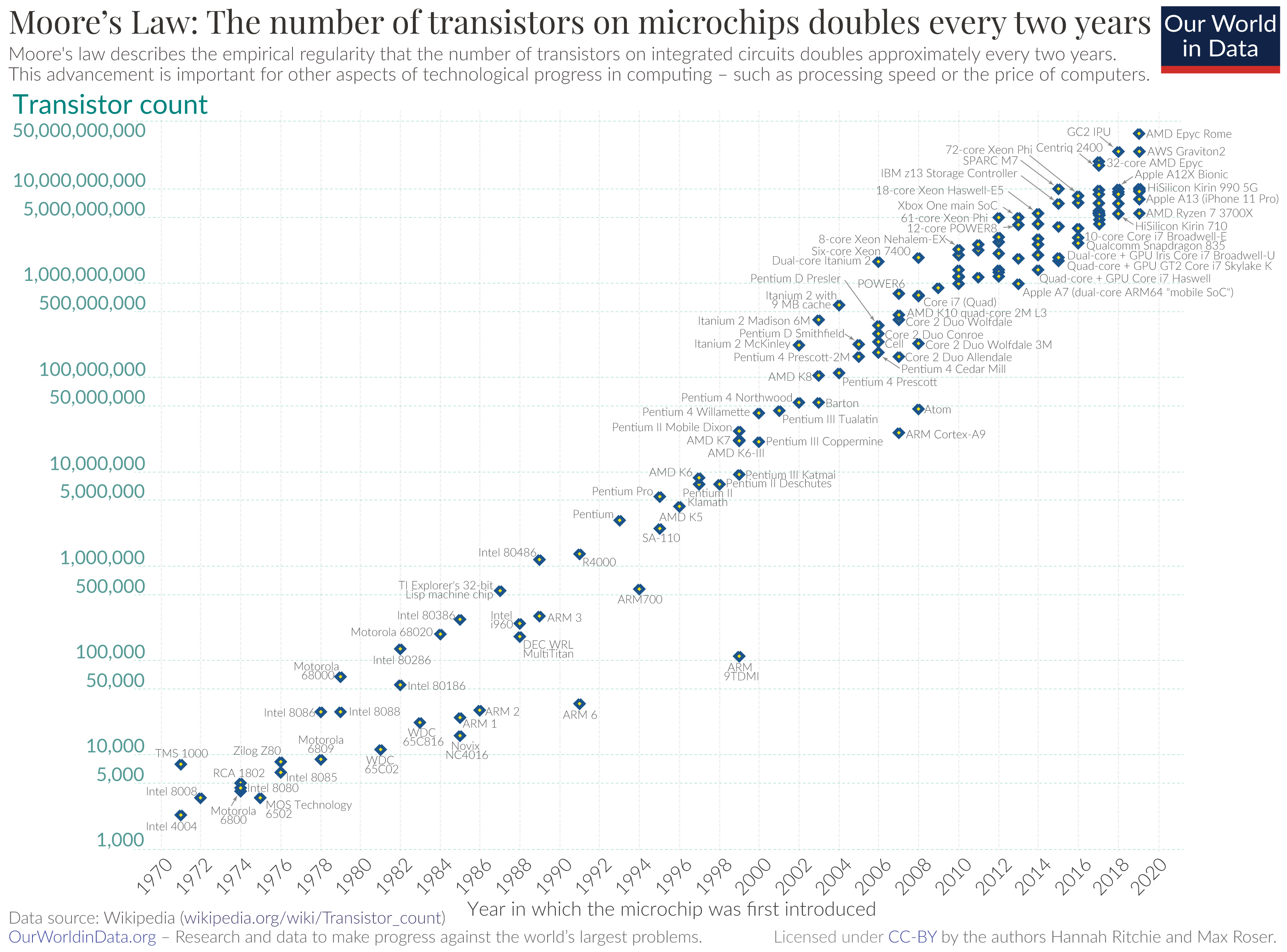

If we think about pennies being like transistors then we can begin to understand the scale.